8. Local Delivery, Injection & Forwarding
Local delivery is considered to be the transfer of a received email to a local INBOX of a known email account in the local system from the MTA's queue. This is subject and responsibility of a Local Delivery Agent (LDA). In case of s/qmail this delivery can be multi-staged; both on a system level, as well on a virtual domain, or personal account level.
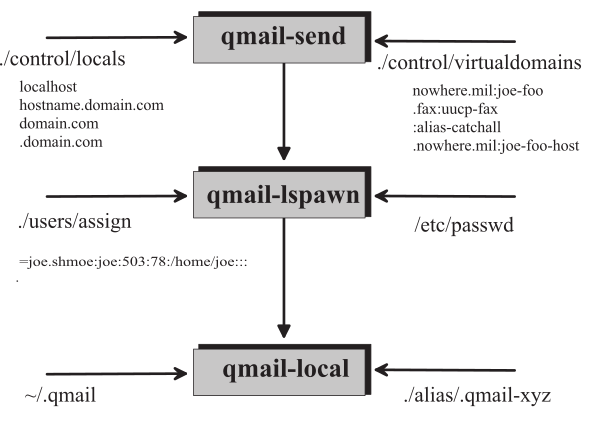
After injecting the email in s/qmail queue, it is treated depending on the domain information given in the Rcpt To: <user@domain.tld> SMTP envelope field according to two mechanisms considering
- locals
- virtualdomains.
To deliver those mails to the users, two processes share responsibility:
- qmail-lspawn and
- qmail-local.
qmail-lspawn is a system process and is enabled to provide an additional s/qmail system's user mapping.
Rather, qmail-local can be advised to include a user-defined second stage delivery process. Here, a user can utilize it for:
- filtering of messages and their content,
- forwarding of emails to other accounts (local and remote)
- invoking other delivery agents like procmail, or dovecot, or others,
- defining the delivery target and format, like mbox or Maildir/.
If nothing particular is provided, the system's defaultdelivery takes place which as given to qmail-start upon start of qmail-send and handed over to qmail-lspawn.
qmail-send will indicate in its logs, how the final delivery took place.
The did_0+0+2 tells how qmail-send was instructed. Here, we have three subvalues separated by the '+':
- The frist value says to how many local users the mail was delivered; in this case '0'.
- The second line parameter, to how many other addresses the mail was transfered; again '0'.
- Finally, the last item indicates the number of programs the mail was subject of: '2'
Quick links:
- 8.1 Acceptance of mails targeting local Accounts
- 8.2 s/qmail local delivery mechanisms
- 8.3 Storage of messages
- 8.4 Email and User Accounts
- 8.5 Local Mail Injection
- 8.6 Mail Forwarding
- 8.7 Mailing Lists
- 8.8 Mail Bounces (QSBMF)
8.1 Acceptance of mails targeting local Accounts
In the s/qmail system, acceptance for emails to local accounts happens under two different conditions, depending whether the email was generated locally or received from an external system.
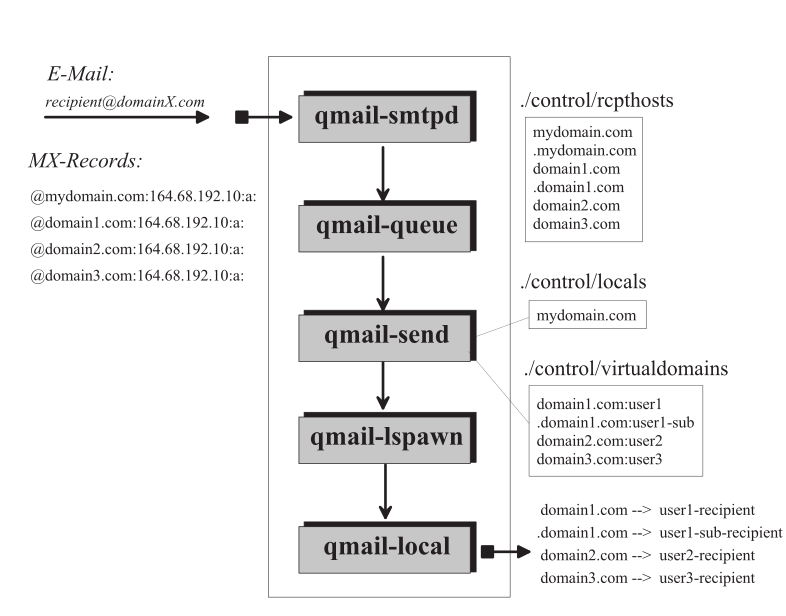
8.1.1 Remote Acceptance for local delivery
In the s/qmail system email arrive from an external originator ('Mail From:' targeting a local recipient ('Rcpt To:') while using
- (E)SMTP(S) services provided by qmail-smtpd or
- QMTP(S) services provided by qmail-qmtpd services
while employing the control files:
- rcpthosts, morecpthosts.cdb and
- recipients
- QMQP service qmail-qmqpd depend on the setting of the tcpserver/sslserver environment variables only.
8.1.2 Local injection
However, emails can be generated locally by means of
- qmail-inject,
- mailsubj, and
- sendmail
and those are not subject of verification; rather they are delivered locally immediately (in case a local address is targeted).
8.1.3 QMQPD injection
Further, emails received via qmail-qmqpd are treated like locally send mails too.
8.2 s/qmail local delivery mechanisms
s/qmail is feature-rich regarding the delivery of local mail. First, let's have a look at the primary mechanisms:
- s/qmail distinguishes between local users (aka regular Unix users) with a home directory and
- virtual users having a parenting Unix user (typically per domain) and some local storage for their mails.
- Qmail has pioneered what is called the 'Variable Envelope Return Path' (VERP) mechanism: Upon reciept the SMTP envelope receiver address ('Rcpt To:') can be extended given the addresses 'local' part (the one before the '@' with a pre-defined token and a customizable prefix. This may happen before and after the user's name (as local part of the address). These prefixes can be stacked.
- Every locally received mail is subject of the 'dot-qmail' mechanism allowing the user to personally define the final delivery instructions. This can can be stacked as well; thus happening at typically at two stages.
Now, let's go into some details, in particular the .qmail (dot-qmail) mechanism.
8.2.2 Local versus Virtual delivery
We already have seen that qmail-lspawn requires and respectes two control files
- locals which has precendence over
- virtualdomains.
If the domain of the received email is not listed in any of those, it is not delivered locally!
Locals: An email received for a domain provided in locals is considered to be delivered for an existing Unix user. However, the provided local part of the SMTP recipient address, may not coincide with the name of the Unix user. This is handled by the qmail-assign mechnism, as default part of qmail-lspawn.
Thus, an email received for therealdonald@whitehouse.gov can be delivered to the Unix user donald (sorry for the example), at this host. Here whitehose.gov needs to be placed in locals.
Virtualdomains: In case whitehose.gov provided in virtualdomains and prepended with an existing Unix user (secretary), say: whitehose.gov:secretary The mail will be delivered to user secretary which is responsible for its final treatment with the now re-written address: secretary-therealdonald@whitehouse.gov.
There exist two popular 'virtual mail manager' packages:
providing management of virtual domains and their users; often accessible via a Web interface and an external user database, either based on SQL or LDAP. A system setup this way is called a Pop Toaster mainly because in the early days, only POP3 services were given. However, an integrated setup is in reach by serveral IMAP servers, namely Dovecot or my BincIMAP. These are supported by s/qmail as well.
Note: The character used to combine the tokens of the local address part can be chosen out of a small set to be defined at compile time of s/qmail. Only characters are useful, which are not part of a general email address, typicalls -, +, =. You can use the configuration file conf-break to provide this initially. In addition, this choice can be overwritten individually by the qmail-users mechanism.
8.2.3 The dot-qmail Mechanism
s/qmail has inherited from DJB's qmail the flexible 'dot-qmail' scheme The basic idea is, that every (local) delivery will be fed thru a particular file in the user's home directory called .qmail[-something]. Here, the user is free to define its own treatment of the incoming mail. Sample .qmail file:
- Local delivery:
- ./Maildir/: The message is delivered here in the Maildir format.
- ./mbox: The message is delivered to this mailbox.
- /var/spool/user: The message is delivered to VSM mailbox owned by user.
- Forwarding:
- &sombody@example.com: Forward mail to this account.
- me@somewhere.else: Forwarding as well.
- Program execution:
- |procmail: Filter through procmail.
- |/usr/local/bin/vdeliver: Call VmailMgr's vdeliver program (for virtualdomains).
Encountering -default is a last resort for matching all other (unresolved) names.
If a dot-qmail file is empty, the defaultdelivery is followed. Local mail delivery thus has a hierarchical complexity, depending on the virtual user taking care for the entire domain(s) and the indivual user. You may allow your users to setup their own delivery mechanisms, for instance filtering of spam messages and setup a vacation notice program.
The .qmail file will be sequentially read and processed by qmail-local Lines beginning with the hash-tag '# will be ignored. If - as a result of the processing - a return code of '99' is encountered, any further execution is stoppped.
Program delivery is subject of qmail-command which provides a lot of (exported) environment variables to be used by the called program or script.
The following programs are coming with s/qmail to be used here:
The man pages provide accurate answers how to use those small programs in your .qmail file.
8.2.4 The VERP mechanism
In qmail and s/qmail the local part of the user's SMTP recipient envelope address is under control of the user and potentially subject of rewriting.
We have already realized, that for virtualdomains, the SMTP envelope recipient address is prefixed with the name for the virtual user. From the above sample: secretary-therealdonald@whitehouse.gov.
However, we simply reverse our view and let now the user append something to the local part of the email address:
This 'appendix' is under control of the user 'me'. DJB has called it 'Variable Envelope Return Path' and can be set differently of every email send from this account. 'apendix123' could be a temporary value, a nonce, a hash, or some other useful information. In s/qmail email addresses with this 'appendix' are treated like the regulary address by the Recipients mechanism.
Later, this procedure was adopted for the 'Bounce Address Tag Validation' (BATV) defined by John Levine and is often used by Postfix. In this case, the SMTP return address of the bounce mail is typically prefixed with a prvs=xyz..=...@... value with chosen delimitor '='.
8.2.5 Applying the VERP mechanism in dot-qmail files
qmail-local enables the user to take advantage of (his own) email VERP addresses. Within the user's home directory - and prior for delivering the mail to its final storage location - qmail-local looks for correspoding dot-qmail file. In the above example, receiving an email for
the following steps are taken out:
- The dot-qmail file .qmail-appendix123 is checked and its instructions are followed.
- If existing, the dot-qmail file .qmail-default is consulted and processed (catch all).
We see, that a standard .qmail file only includes delivery instructions for the basic email address. In case VERP addresses are used, a matching dot-qmail file a .qmail-default has to exist.
8.2.6 Environment Variables provided at Delivery
Upon the delivery of the received message to the users mailbox (in any format) qmail-local populates the following environment variables, which can be used by the following programs and local MUAs:
| qmail-local environment variable | Meaning |
| $SENDER | Asdress of SMTP envelope sender. | $NEWSENDER | SMTP sender address of the forwarding path. |
| $RECIPIENT | Address of recipient of the SMTP envelope given as: local@domain. |
| $USER | Recipient in the Unix system./td> |
| $HOME | Home directory of recipient./td> |
| $HOST | Domain part of the recipient address. |
| $HOST2 | Part of FQDN before the last dot (gtld). |
| $HOST3 | Part of FQDN following the last dot (domaind). |
| $HOST4 | Part of FQDN following the next dot (hostname). |
| $LOCAL | Local (user) part of the SMTP address. |
| $EXT | Qmail extension. |
| $EXT2 | Part of Qmail extension following the first delimitor. |
| $EXT3 | Part of Qmail extension following the second delimitor. |
| $EXT4 | Part of Qmail extension following the third delimitor. |
| $DEFAULT | Name of "default" extension of the dot-qmail default file, typical .qmail-default. | $DTLINE and $RPLINE | Content of the "Delivered-To:" and "Return-Path:" in the message header. |
| $UFLINE | UUCP From_: format; appended by qmail-local for mbox delivery. |
8.2.7 Dot-qmail with virtual Accounts
Considering a case where a virtual account (a primary Unix account) is responsible to deliver email for its domain with several virtual users.
This primary account has a virtual user - let's call it eve - to be subject of individual delivery to its mail account. This is possible with the specific dot-qmail file in the home directory of the principal account as:
- .qmail-eve
- .qmail-eve-default
Given the last instruction, even all sub-ordinary VERP-addresses of eve are now considered as well.
8.3 Storage of messages
In general, emails are treated as files in the following ways:
- They are stored on the local file system,
- they stored on a remote file system mounted by means of NFS, SMB, or other mechanism making the file system appear to exist locally,
- they could be transferred to a remote file system upon receipt.
Persistent storage of email messages follows typically the following historical rules:
- the message is stored on a common space on the file system known as VSM (var-spool-mail) as concatinated files in the so-called mbox format.
- The message ist stored in the mbox in the user's home directory,
- the email messages are stored in the recipient's directory as individual files following DJB's maildir format.
- This can be extended as maildir++ which is compatible with the Maildir format.
qmail-local supports all of the various mechanisms; either by the
- defaultdelivery as defined by qmail-start, - or -
- by individual settings of a local user as provided in a his/her .qmail file.
8.3.1 User Quotas
s/qmail does not have a notion of quotas, thus they have beeen externally supplied and defined. Quotas are supported by
using separate programs. In addition and using IMAP as access protocol to local Mailboxes, the IMAP server has to understand the concept of quotas.
8.3.2 Email Backup
Most countries require for companies to have a working solution for email backups. It is clear, that the Maildir format has intrinsically all the merits you want to have to save and backup our emails on-the-fly without any concern of potentially incoming new mails:
- The Maildir format guarantees that every mail is one singe file and unique even over several machines.
- The state of the email is indicated as suffixes to the email/message itself.
Using BincIMAP here on my system, I get the following listings of my mails under Maildir/cur:
Every mail can be easly 'grepped' for its content and backuped indivdually. Check DJB's explanation about that format: Maildir.
8.4 Email and User Accounts
We now need to identify in the first place, who can eventually receive email, thus is qualified for reception. Email recipient accounts in the s/qmail system may be distinguished as:
- Local managed accounts:
- Local Unix user
- s/qmail 'alias' mechanism
- s/qmail 'assigned' user
- Virtual managed accounts:
- Remote managed accounts:
- Mailing Lists
- EZMLM
- Majordomo ??? (no useful Internet presence any more)
8.4.1 Unix users and the Assign Mechanism
The SPAMCONTROL patch was written in mind for a MTA being just a 'hub' on the Internet receiving and sending mails for some second tier (downstream) mail servers. In fact, Novell's GroupWise was the major customer here. Exchange and Lotus Notes (Domino) were also important players. In this context, the only relevant 'local' users were root (for administrative tasks) and the postmaster taking responsibility for mail delivery.
Rather, s/qmail can be used on a Unix system with few or many users. DJB considered this use case in the following way:
- A user must have an email address, targeting (by means of a MX record) at least his/her domain.
- The email address must be mapped to a local user on the Unix system in order be able to be delivered. This task can be accomplished by the assign mechanism. In case, the local part of the mail addresss (the recipient) does not match a local Unix user name a mapping is required.
Description ($QMAIL denotes the s/qmail home directory):
| Location | $QMAIL/users/assign.cdb (clear text), $QMAIL/users/assign.cdb (compiled) |
| Simple assignment | =local:user:uid:gid:homedir:dash:ext: |
| Wildcard assignment | +loc:user:uid:gid:homedir:dash:pre: |
| Closing statement | . |
| Generation | $SQMAIL/bin/qmail-newu (users/assign needs to exist) |
| Advanced generation | $SQMAIL/bin/qmail-pw2u < /etc/passwd (takes users form /etc/passwd and generates the assign file. After verification and adjustments, call $SQMAIL/bin/qmail-newu |
| Recognition upon receipt | If a domain name in control/recipients includes '=' after the colon ':' (example.com:=) assign.cdb will be consulted for valid users by qmail-smtpd |
| Recognition upon delivey | qmail-lspawn will automatically evaluate this file and deliver emails accordingly |
Ingridients of the assign file:
- =local: This is the SMTP email address.
- +loc: This the VERP email address before the delimitor (wildcard).
- user: Is the Unix user.
- uid: Is the Unix user's UID.
- gid: Is the Unix user's GID.
- homedir: Is the Unix user's home directory.
- dash: Is the Unix user's delimitor used.
- ext: Is the Unix user's extension in place.
This mechanis provides maximum control given incoming mails. However, the Recipients mechanism does not support 'wildcard' support here.
8.4.2 The Alias User
In the (s/)qmail system there is only one 'living' account: The Alias user.
The Alias has typically its home directory typically at /var/qmail/alias and is responsible for the treatment of email sending/forwarding/reception for which no other local user is dedicated for.
The Alias user acts on behalf of the following none-existing accounts:
- MAILER-DAEMON: The Mailer Daemon is responsible to generate bounce message. However, a double bounce maybe the result. In order to process those a 'real' user, within .qmail-MAILER-DAEMON a forwarding address can be specified.
- Postmaster: The postmaster takes care for the entire MTA. Mails to this account should be forwarded to an existing accout by means of .qmail-postmaster; otherwise it will be discarded.
- Root: A security concept of qmail is, that the (impersonal) 'root' user (UID=0) in the Unix system is never target by mails directly; rather it is required that this task is dedicated to a personal account using a forwarding instruction in .qmail-root.
In practice, .qmail-root is very imporant because system message (i.e. disk failure messages) are directed to this account by some service software.
Using the EZMLM mailing listing manager, the entire reception of emails is realized via the Alias user making significant use of the VERP mechanism.
8.5 Local Mail Injection
Within s/qmail we have the following moduls allowing to inject messages into the queue:
- qmail-inject - the main program
- sendmail is s/qmail's wrapper for qmail-inject supporting some important commands of the original sendmail to be compliant with it, which is required by lots of other programs.
- mailsubj is again a very small wrapper around qmail-inject reading the message on FD 0 and including the subject given following be the recipients.
Common with all these programs is the understanding of environment variables given prior of their call. In particular the sender can be qualified by the following attributes:
| qmail-inject environment variable | Meaning |
| $QMAILUSER, $MAILUSER, $USER, or $LOGNAME | Name in "From:" header field. |
| $QMAILHOST or $MAILHOST | Hostname within the "From:" header field, typically the value taken from control/defaulthost. |
| $QMAILNAME, $MAILNAME or $NAME | The personal name in the field "Sender:" of the header. |
| $QMAILSUSER and $QMAILSHOST | The sender information given in the SMTP "Mail From:". |
| $QMAILMFTFILE | List of email addresses (one per line) beeing subject of delivery. |
A more fine-grained behavior of qmail-inject can be achieved by means of a set of additional environment variables which are structured as typical arguments:
| $QMAILINJECT | Consequence | Meaning |
| c | Comment address style | Normal format of the comment line in "From:" field; just the address. |
| s | Set Return-Path | No evaluation of the "Return-Path". Usually, the "Return-Path" is the SMTP sender address without considering other environment variables. The header "Return-Path" will be removed. |
| f | From: | Removes all "From:" header. Usually, the "From" field will be replaced by qmail-inject. |
| i | Ignore Message-ID | Removel of the "Message-ID" field; otherwise compliant to option f. |
| r | Per-Recipient VERP | Per recipient an "Variable Envelop Return Path" VERP will be generated, including in the "Sender" field additionally the value of the recipient (Send: Sender-Recipient). |
| m | Per-Message VERP | Per email a VERP address will be generated including in the "Sender" field the current data and PID of the process. |
8.5.1 s/qmail's sendmail interface
In the original qmail DJB did not provide any man page for his sendmail clone. Some criticism came for Matthias Andree (see: The DJB Way, and here: Way back engine) for not providing some relevant sendmail flags.
The sendmail flags supported in s/qmail are:
- -t: read the CC: and BCC: and include those as recipients.
- -f: the sender.
- -F: the FULLNAME of the sender.
- -ba, -bm: read the queue ( qmail-qread).
- -bs: invoke qmail-smtpd for sending.
Most other sendmail arguments are simply ignored. However, in case of none-ignored argument, sendmail will issue this warning and quits:
Like the standard sendmail here the (pre-formated) message is read from FD 0 and all further arguments (apart from the those mentioned) are interpreted as SMTP recipient addresses.
8.6 Mail Forwarding
Though mail forwarding is a particular notion of mail injection because historically it has some importance and a lot of mechanism were provided to fullfill this task of 'spreading out the news'. Thus, there is no surprise, that s/qmail not only includes the vanilla qmail mechanisms but also incorporate the entire fastforward package.
In fact, s/qmail supports:
- Simple Forwarding the the dot-qmail mechanism.
- Forwarding by the forward instruction in a dot-qmail file.
- Forwarding by alias files here available as newalias.
- Advanced forwarding based on fastforward.
8.6.1 Simple Forwarding
Upon email recipt, the dot-qmail may include forwarding instructions in a simple way:
Here, the order of execution is important. If one executions fails with RC=99, all following ones are discarded, thus the message would never be delivered if this happens on the first line.
Typically, the forwarded message retains the original email SMTP sender address. However, this may be subject of change. If the above case - with an exisiting special tailored file .qmail-me (me could be any extension name) - an additional dot-qmail file like
has been given, the forwarding email address for myboddy is now local-mybuddy and not the original one. In the above case, we assumed that the original email is targeting the (local) user with the extension me and the hostnames are given by the control file defaultdomain. However the forwarding instruction can be generalized by using a .qmail-default file in the first place.
8.6.3 Explicit forward Instruction
The previous usage of forwarding in a dot-qmail file assumes that the recipient subject of forwarding the email to is already known by his/her address.
Using forward instruction in a dot-qmail allows to relax this condition and use a forged forwarding address on the fly:
In this case - prior of delivery - an additional script my_forwarding_script.sh is used to evaluate the via qmail-command given environment variables the incoming emails and set the forwarding addresses $address1 and $address2 on-the-fly. This allows an 'on-demand' forwarding and use of email messages in a delivery workflow chain.
8.6.2 Newaliases and Newinclude
In the 'good old' sendmail days forwarding of email was subject of the alias mechanism. Here, a file /etc/aliases exists including recipies for mail forwarding in the format:
These forwarding rules are cumulative, thus email loops are possible. By definition, this 'database' is public and shared. In s/qmail the command newaliases can be used to turn this 'database' into a cdb:
This compiled database can be be used by the fastforward mechansim.
The files /etc/aliases may contain additional delivery instruction provided in a external file via the :include:file statement:
Using newinclude this file again is converted into a binary format:
8.6.4 Fastforward
fastforward is suited to deliver mails given their addresses are include in well-formed fastforward cdb database to their SMTP recipients.
Apart from newinclude, fastforward comes with two helper programs:
- setforward and
- printforward.
The fastforward database can be used efficiently given two different purposes:
- The usual case it within a dot-qmail file: &ver;fastforward addresses.cdb.
- The database address.cdb can be used within qmail-smtpd Recipients mechanism, in case the MTA is used as forwarding mail server only and while used as hop in the Internet email infrastructure.
It should be noted, that fastforward does not resend any mail, but rather re-writes the recipient SMTP address in the queue. Therefore, the message is not copied in the first place, which makes fastforward very efficient.
8.7 Mailing Lists
s/qmail comes with a 'poor's man' mailing list feature, which is based on the fastforward mechanism as well.
Again, providing a set of email addresses in a file simply as:
This file can now be processed by:
- setmaillist and
- printmailist.
According to newinclude, setmaillist can read a file mailings from input resulting in a mailings.bin as binary file while evaluating and including a file (if given with a prepending slash or dot) named in the example as otherrecipients. The correctness of this operation can be controlled invoking printmailist and comparing the output.
Of course, this is a very simple mailing list only and not able to handle subscriptions or bounces adequately. But if you have a small group of people you need to address by email, this mechanism can be used in again a dot-qmail- file:
Given the file mailings.bin has been successful generated, an email targeting a user's address with the VERP extension mailinglist will advice fastforward to forward the incoming mail to all recipients given in the original file mailings.
8.8 Mail Bounces (QSBMF)
In case an email can not be delivered (locally or remotely) because reception is refused due to several reason, qmail-send generates a bounce message and tries to deliver it to the originator of that mail.
Here, s/qmail commen with qmail uses the Qmail Send Bounce Message Format QSBMF together with an indiciation of the delivery error while copying the verbose error message from the targetted MTA in the bounce message. The SMTP envelope sender of a bounce message is always empty: MAIL FROM <>.
In case, these bounce message can not be delivered (mainly because the originator's address is wrong or faked) a double bounce will send to the postmaster of the originator's MTA (which even might not exist) and finally a triple bounce is created and finally dropped.
s/qmail has several ways to deal with bounces:
- control/bouncefrom let you set to name of bounce sender; typically MAILER-DAEMON.
- control/bouncehost is the hostname of the bounce host, which could be different from the usual hostname, in order to manage double bounces separately.
- control/bouncemaxbytes allows to truncate the size of the QSMBF bounce message. This is in particular useful for MTAs with a data size limit in order to avoid bounce bouncing.
- control/doublebouncehost is the hostname used here.
- control/doublebouncefrom is purtorted sender name, usually postmaster.
- control/smtproutes and control/qmtproutes can be instructed to send bounces to a particular bouncehost by simply including a !@:bouncehost here.
These settings are tasks of the 'real' postmaster; no user-intervention is required here.
